Are you excited about 2D vs 3D video games? To develop 2D or 3D games, you should know the biggest difference between 2D vs 3D video games. For decades, the gaming industry has been on a constant journey to development. From the 2D games in the first years to the very engrossing 3D world that dominates today, technological progress has changed gaming experience.
However, many predicted that the rise of 3D would completely exclude the 2D games, both styles continue to flourish, each with their strength and dedicated player base.
In this blog we take you to the major differences between 2D and 3D games, their unique applications and development processes behind them. Whether you are a game developer who will choose the right style for your project or anxious gaming enthusiasts on the development of video games, this guide will provide valuable insights.
The Rise of 2D Video Games
3D graphics before becoming a reality, 2D gaming ruled the top. The classic arcade titles such as Pac-Man, Super Mario Bros and Street Fighter gave shape to the basis for the industry. These games depended on pixel art, side scrolling mechanics and limited animation frames to create attractive experiences. At that time, due to technical barriers, gaming developers had no choice but to work within the bounds of the 2D environment.
However, instead of having a limit, the 2D design showed being a property. It provides the opportunity to easily see game mechanics, accurate control and visually attractive art styles that still have indifferent values. Even modern hits like Hollow Knight and Celeste showed their ongoing appeal when the technology was advanced.
The Emergence of 3D Graphics
The Mid -1990s had a twist with the introduction of 3D games. Titles such as Super Mario 64 and The Legend of Zelda: The Legend of Zelda: Ocarina of Time, the game design by presenting more understanding of open world exploration, dynamic camera angles and realism. Whereas, players can now move regardless of the expansion environment, interact with complex physics and experience more engrossing storytelling.
As 3D technology developed, sports were quickly refined. The developers began to integrate movement catches, realistic physics engine and AI-operated interactions, as further blurry lines between reality and virtual world. Today, 3D games such as Eldon Ring and Cyberpank 2077 set new standards for engrossing gaming experiences.
Ready to Develop Your Own 2D or 3D Game?
Whether you’re diving into classic 2D gameplay or pushing the limits with 3D graphics, our game development experts can bring your vision to life. Get professional guidance on the best approach for your project!
Hire Expert
Key Differences Between 2D VS 3D Games
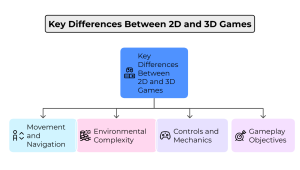
Here are the key differences between 2D vs 3D games:
1.Movement and Navigation
2D Games:
Movement is primarily restricted to a linear plane, meaning characters move left, right, up, or down, often within a side-scrolling or top-down perspective. This structure is commonly seen in platformers like Super Mario Bros. or puzzle games like Tetris.
3D Games:
Players have unrestricted movement, allowing them to explore environments in multiple directions. Games like The Legend of Zelda: Breath of the Wild or Grand Theft Auto V offer open-world experiences with greater interactivity.
2. Environmental Complexity
2D Games:
The focus is typically on gameplay mechanics rather than detailed environments. Backgrounds and scenery are often static or minimally interactive.
3D Games:
These games provide highly detailed worlds, complete with dynamic environments, realistic lighting, and interactive elements that enhance immersion.
3. Controls and Mechanics
2D Games:
Simplicity is key. Controls are often intuitive, making 2D games more accessible to casual players. Jumping, running, and attacking are performed using a few basic buttons.
3D Games:
With increased freedom of movement, controls become more complex. Players may need to manage camera angles, perform intricate actions, and navigate detailed landscapes, requiring a higher level of skill and coordination.
4. Gameplay Objectives
2D Games:
Goals tend to be straightforward, often revolving around reaching a specific endpoint or achieving a high score. Classic examples include Pac-Man and Flappy Bird.
3D Games:
These games often have more intricate objectives, including mission-based gameplay, exploration, puzzle-solving, and interactive storytelling. Examples include Skyrim and The Witcher 3.
People Also Read: Top 60 Mobile Game Development Ideas for 2025
Game Development Stages: From Idea to Release
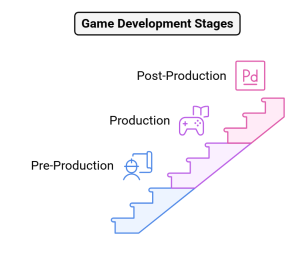
2D vs 3D Game development is structured into three major phases:
1. Pre-Production: Laying the Foundation
This is the planning stages for 2D vs 3D, where all critical decisions about the game are made. It involves:
- Defining the game concept (genre, storyline, mechanics, target audience).
- Selecting the game engine (Unity, Unreal Engine, Godot, etc.).
- Outlining the art style (2D pixel art, vector art, or 3D models).
- Budget estimation and resource allocation.
- Creating initial prototypes and storyboards.
For both 2D vs 3D games, pre-production sets the stage for smooth development by resolving potential challenges early on.
2. Production: Turning Ideas into Reality
This is the most extensive phase where the game takes shape. Key tasks include:
Art & Graphics Development:
2D Games: Character design, backgrounds, UI/UX, and animations using tools like Photoshop, Illustrator, or Spine.
3D Games: 3D modeling, rigging, texturing, and animations using Blender, Maya, or ZBrush.
Programming & Game Mechanics:
- Developers integrate the assets into the game engine and code game logic, AI behaviors, and interactions.
- 2D games often have simpler mechanics compared to the more complex physics and movement systems in 3D games.
Music & Sound Design:
Background music, sound effects, and voice acting are created and added to enhance the gaming experience.
3. Post-Production: Final Touches & Updates
Once the game is playable, the post-production phase ensures it runs smoothly before release. This stage includes:
- Bug fixing & Optimization: Resolving glitches, improving performance, and optimizing the game for different platforms.
- Testing & Quality Assurance: Playtesting for stability, functionality, and user experience.
- Game Launch: Marketing campaigns, app store submissions, and official release.
- Post-Launch Support: Patches, updates, and possible expansions based on player feedback.
In addition to these stages, testing, pre-launch marketing, and final launch preparations play a crucial role in a game’s success.
2D vs. 3D Game Development Team: Who’s Involved?
Developing a game requires a specialized team of experts. While the team composition might vary depending on the scope and complexity of the project, here are the key roles involved in both 2D game development and 3D game development:
Game Producer: Oversees the entire project, ensuring deadlines and budgets are met.
Game Designer: Develops game mechanics, level design, and overall gameplay structure.
Artists:
- 2D Artists for 2D games (concept art, character design, UI).
- 3D Artists for 3D games (modeling, texturing, animations).
Developers (Programmers): Implement gameplay logic, physics, AI, and multiplayer functionalities.
Testers & QA Specialists: Identify and report bugs, ensuring a seamless gaming experience.
Project Manager: Organizes workflow, monitors progress, and maintains communication between teams.
Larger game studios may have additional specialists such as narrative designers, technical artists, and VFX artists, especially for complex AAA 3D games.
Build Your Dream Game with Expert Developers
From 2D classics to cutting-edge 3D experiences, our specialized game development team is ready to bring your vision to life. Get in touch with our experts today!
Hire Expert
How Long Does It Take to Develop a 2D vs. 3D Game?
The timeline for game development depends on factors like game size, level of detail, and complexity.
2D Games: Typically take 3 to 12 months for indie or mid-sized projects.
3D Games: Require 1 to 3 years or more, especially for high-end projects with detailed environments and mechanics.
Which Type of Game is Right for You?
The choice between 2D and 3D depends on factors such as game design complexity, budget, and target audience:
For beginners: 2D games are easier to develop, making them a great starting point for indie developers and small studios.
For immersive experiences: 3D games provide a richer visual and interactive experience, making them suitable for adventure and open-world genres.
For casual gameplay: 2D games often have simple mechanics, making them ideal for quick, engaging sessions.
For expansive storytelling: 3D environments allow for deeper narratives and complex interactions between characters and the game world.
Game Engines for 2D and 3D Game Development
Game engines are the backbone of the game development process, providing developers with the necessary tools to bring their creative visions to life. Whether designing a 2D platformer or a highly immersive 3D adventure, choosing the right engine is crucial. In this guide, we’ll explore some of the most popular game engines used for 2D and 3D game development, highlighting their key features and capabilities.
Top Game Engines for 2D and 3D Games
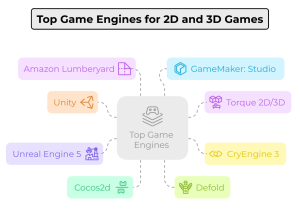
1. Unity – A Versatile Powerhouse
Unity is one of the most widely used game engines due to its user-friendly interface, cross-platform support, and robust asset store. It supports both 2D and 3D game development, making it a go-to choice for developers at all skill levels.
Ideal for: Indie developers, mobile games, and AAA projects.
Key Features:
- Extensive library of pre-built 2D and 3D assets.
- Strong community and extensive documentation.
- Supports multiple programming languages, including C#.
- Flexible rendering system for realistic graphics.
2. Torque 2D/3D – Beginner-Friendly Development
Torque 2D/3D is an excellent option for those new to game development. It offers a scripting language and visual editing tools, allowing developers to create interactive levels with ease.
Ideal for: Beginners and small indie projects.
Key Features:
- Supports both 2D and 3D game development.
- Customizable engine with open-source flexibility.
- Multi-platform deployment.
- Well-documented scripting system for custom game mechanics.
3. CryEngine 3 – High-End Graphics for AAA Games
CryEngine 3 is known for delivering stunning visuals and advanced physics. It is widely used in AAA game development, particularly for first-person shooters and open-world games.
Ideal for: High-budget projects requiring realistic environments.
Key Features:
- High-fidelity rendering for ultra-realistic graphics.
- Powerful physics engine for realistic object interactions.
- Advanced AI and animation tools.
- Free-to-use model with royalties on commercial projects.
4. Unreal Engine 5 – The Industry Giant
Unreal Engine, developed by Epic Games, is one of the most advanced game engines available. With the release of Unreal Engine 5, it has introduced groundbreaking features like Nanite (a virtualized geometry system) and Lumen (a global illumination system).
Ideal for: AAA developers, VR projects, and highly detailed 3D games.
Key Features:
- Nanite allows for real-time rendering of millions of triangles.
- Lumen enables realistic dynamic lighting.
- Blueprint visual scripting system for non-programmers.
- Cross-platform capabilities, including PC, console, and mobile.
5. Cocos2d – A Top Choice for 2D Games
Cocos2d is a lightweight engine popular among indie developers and mobile game creators. It supports multiple programming languages such as Python, Lua, and JavaScript, making it highly flexible.
Ideal for: Mobile and indie 2D games.
Key Features:
- Built-in physics engines for realistic object movement.
- Strong support for 2D animations and sprite rendering.
- Open-source framework with an active developer community.
- Optimized for performance on low-end devices.
6. Defold – Lightweight Yet Powerful
Defold is a compact but powerful engine that supports both 2D and 3D game simulations. It is particularly popular for its Lua-based scripting language, allowing for seamless game logic implementation.
Ideal for: Indie game developers and small studios.
Key Features:
- Built-in physics engine for smooth object interactions.
- Advanced animation support for dynamic visuals.
- Particle effects system for eye-catching visual effects.
- Efficient performance, making it ideal for mobile games.
7. Amazon Lumberyard – Cloud-Integrated Development
Amazon Lumberyard stands out due to its seamless integration with Amazon Web Services (AWS), enabling cloud-based game hosting and multiplayer support.
Ideal for: Multiplayer games and cloud-based development.
Key Features:
- Script Canvas for visual scripting.
- Advanced terrain editor and character creation tools.
- Easy scalability with AWS cloud solutions.
- Built-in support for real-time multiplayer game development.
8. GameMaker: Studio – Intuitive & Beginner-Friendly
GameMaker: Studio is perfect for developers with little programming experience, offering a drag-and-drop interface alongside a custom scripting language (GML) for added flexibility.
Ideal for: 2D platformers, RPGs, and indie games.
Key Features:
- Simple interface for quick prototyping.
- GML scripting for advanced customization.
- Asset marketplace with ready-made sprites and sound effects.
- Strong community support for beginners.
Why Do Gamers Prefer 3D Games Over 2D Games?
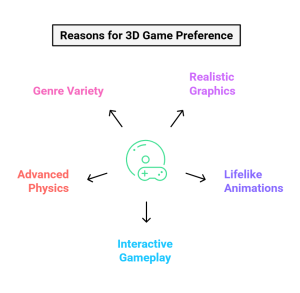
While 2D games hold a nostalgic charm, 3D games provide an immersive and engaging experience that many gamers prefer. Here are some of the reasons why:
1. Realistic Graphics & Environments
Advancements in 3D rendering technology have enabled game developers to create highly detailed environments that make players feel as though they are inside the game world. The depth, lighting, and textures in 3D games provide a cinematic experience that 2D games cannot replicate.
2. Lifelike Animations
Character animations in 3D games have become incredibly realistic, from fluid movements to intricate details like hair physics and cloth simulation. This level of realism enhances immersion, making gameplay feel more natural and dynamic.
3. Interactive Gameplay & Exploration
Unlike 2D games, which are typically limited to side-scrolling or top-down views, 3D games offer open-world exploration, allowing players to move freely in all directions. This leads to more engaging and unpredictable gameplay experiences.
4. Advanced Physics & Mechanics
3D games utilize real-world physics engines to create realistic interactions between objects, such as:
- Gravity simulation.
- Object collisions and destruction.
- Environmental effects like water movement and weather dynamics.
5. Greater Variety in Game Genres
While 2D games are mostly found in genres like platformers, puzzle games, and arcade games, 3D technology enables the development of a wider range of genres, including:
- Open-world RPGs (e.g., The Elder Scrolls: Skyrim).
- First-person shooters (e.g., Call of Duty).
- Racing simulations (e.g., Forza Horizon).
- Virtual reality (VR) games.
Final Thoughts
Both 2D vs 3D games development have distinct benefits, suited to varying styles, budgets, and experiences of gameplay. While 2D games are still cherished because of their simplicity and ease of access, 3D games keep the boundaries of realism and immersion expanding. As a prospective developer or even a devoted gamer, realizing such differences will allow you to appreciate the progression of gaming as well as select the correct route for your next project.
Also Read: 30 Best Offline iPhone Games That Don’t Need Internet.
FAQs















